Midwife vs. OB-GYN: What’s The Difference?
Pregnancy and birth can be a transformative experience and it is important to have the right healthcare provider to guide you through that journey. There are two types of clinical providers that pregnant people can choose from during their pregnancies: midwives and obstetricians/gynecologists (OBGYNs). While both providers seek to support pregnant people through a healthy pregnancy and delivery, there are differences between the two worth exploring before deciding which provider is right for you.
What is a midwife?
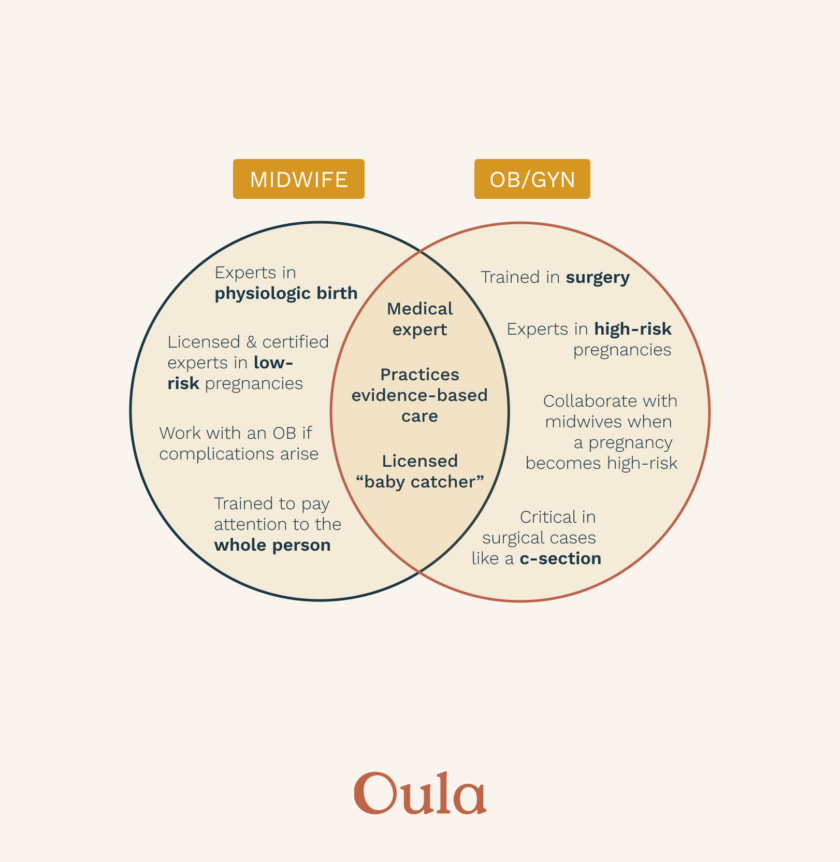
We like to say that everyone needs a midwife and some people need a doctor, too. Midwives are licensed and certified medical practitioners with particular expertise in low-risk pregnancies and childbirth. Importantly, midwives are educated and trained to pay particular attention to the “whole person,” taking a holistic approach to prenatal care. Many people feel judged or dismissed by their care providers today, but midwives work to understand how a person’s needs and their health are intertwined with their family, community, work, and their home.
What Do Midwives Do? (what makes midwifery care unique)
The midwifery model of care centers itself around the idea that pregnancy is not a medical condition but a healthy and exciting experience that the body is capable of. Midwives take a holistic approach to prenatal care placing a significant emphasis on trusting the body’s instincts in childbirth and safely minimizing medical interventions. Midwives typically provide a more personalized and intimate approach to care, focusing on the emotional and physical needs of the birthing person while still performing evidence-based clinical care. They emphasize the importance of natural laboring techniques such as positioning of the body, breath work, meditation, and creating space and time for the body to find a steady rhythm in labor. Research around the efficacy of midwifery care indicates lower rates of medical intervention, including C-sections, induction of labor, and the use of operative vaginal techniques such as forceps or vacuum.
What is an OBGYN?
Just like midwives, OBGYNs are skilled, licensed, and certified medical professionals, yet they offer their services to both low and high-risk pregnancies. OBGYNs have gone to medical school and are experts in surgery and high-risk prenatal care and births, critical in cases where a surgical intervention like a c-section is necessary.
What Do OBGYNs Do? (what makes OBGYN care unique)
OBGYNs tend to have a more clinical and medical approach to care. They focus on managing the physical aspects of pregnancy and childbirth. Having had extensive training as physicians in high risk obstetrics, their scope of practice includes management of chronic medical conditions in the context of pregnancy and/or obstetrical complications that require medical intervention for safety of the birthing person and fetus.
What are the main differences between a midwife and an OBGYN?
Midwives and OBGYNs differ in a number of ways including education, training, scope of practice, and philosophical approach to care.
Midwife and OBGYN education and training
In the United States, Certified Nurse Midwives (CNMs) start as registered nurses (RNs) and then follow up with a Master’s degree in midwifery. Much of the training model is the same as that of Nurse Practitioners (NPs) in other fields of medicine. Midwifery clinical training explores evidence-driven medical and non-medical care for low to high risk OBGYN conditions but places a heavy emphasis on supporting normal physiology of pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period. Certified Midwives (CMs) have a bachelor’s degree in a related field, followed by a Master’s degree in midwifery and similar clinical training as CNMs. Read more about What actually is a midwife?
OBGYNs are medical doctors who specialize in reproductive and gynecological healthcare. They have completed medical school, followed by a specialized residency program in obstetrics and gynecology. They have expertise in managing high risk pregnancies and gynecological care through medical and surgical interventions.
Scope of practice
Midwives and OBGYNs are both trained to provide full-scope obstetrical and gynecological care including performing annual wellness exams (including pap smears), testing for and treating STDs and other infections, prescribing birth control, addressing gynecological concerns like abnormal uterine bleeding, endometriosis, and fibroids, evaluating postmenopausal patients, performing prenatal and postpartum care, and attending deliveries.
Midwives focus on providing care to individuals with low to moderate risk pregnancies, typically working with pregnant people who are anticipating a normal vaginal delivery and do not have complex pre-existing medical conditions. Midwives do not perform surgeries, though some assist OBGYNs in surgical procedures.
OBGYNs on the other hand have a broader scope of practice that includes managing high risk pregnancies and performing surgical procedures. Their training allows them to work with individuals with increased risk factors like chronic illnesses or pregnancies identified as having increased complications. OBGYNs have the expertise to perform surgical interventions such as C-sections, hysterectomies, and other gynecological surgeries.
Both types of providers may perform care in clinics, hospitals, birthing centers, or in the birthing person’s home depending on their approach to care. Both types of providers typically do take medical insurance, but this is provider dependent.
The next sections will describe more about the differences in their philosophical approach to care.
Midwife vs. OBGYN for pregnancy care
As a pregnant person, there are benefits to exploring both care from a midwife vs. OBGYN.
People who seek out midwives often are searching for a holistic, low-intervention approach to birth. In the United States, most midwives attend deliveries in a hospital where the birthing person can labor/deliver in a holistic and low-intervention environment while still having access to medical pain management (including an epidural) and a backup OBGYN team and operating room if medically necessary. Some pregnant people who are apprehensive of delivering in a hospital may seek out midwifery care if they wish to deliver in a birthing center or at home (Oula’s midwives currently do not work within a birthing center and do not attend home births).
Those that would prefer to receive care from a provider who has more expertise in high risk prenatal care or know that they must deliver via Cesarean may seek out care from an OBGYN practice.
Some practices recognize that there are benefits to having both types of practitioner involved in your care and offer care through a collaborative team of midwives and OBGYNs. Oula’s approach to maternity care offers a version of this hybrid approach. While your prenatal care and delivery will largely be attended by a group of midwives, Oula’s doctors are available for consultation and operative intervention as necessary. Learn more about what we mean by “collaborative” care at Oula.
How to Decide Which Provider Is Right For You
Midwives and OBGYNs both play similar and important roles in ensuring a healthy pregnancy and delivery. Midwives provide a more natural and holistic approach to care, while OBGYNs have a broader scope of practice that includes managing high risk pregnancies and performing surgical interventions. Ultimately the choice of which provider will depend on each person’s individual preferences, risk level, medical history, and the specific details of their pregnancy as well as health insurance coverage. They must also take into account where they plan to give birth, and their preferred method of pain management and delivery. Whether you seek care from a midwife, an OBGYN, or a collaborative team of both, labor and birth can be a beautiful experience. An empowering and fulfilling pregnancy and birth can be achieved no matter which type of provider attends your delivery.
